Is AI pushing the enemy advance line using knowledge loops?
Is AI using Mao Zedong’s teachings to advance and gain territories from the human realm?
AI is definitely using the human in the loop to win.
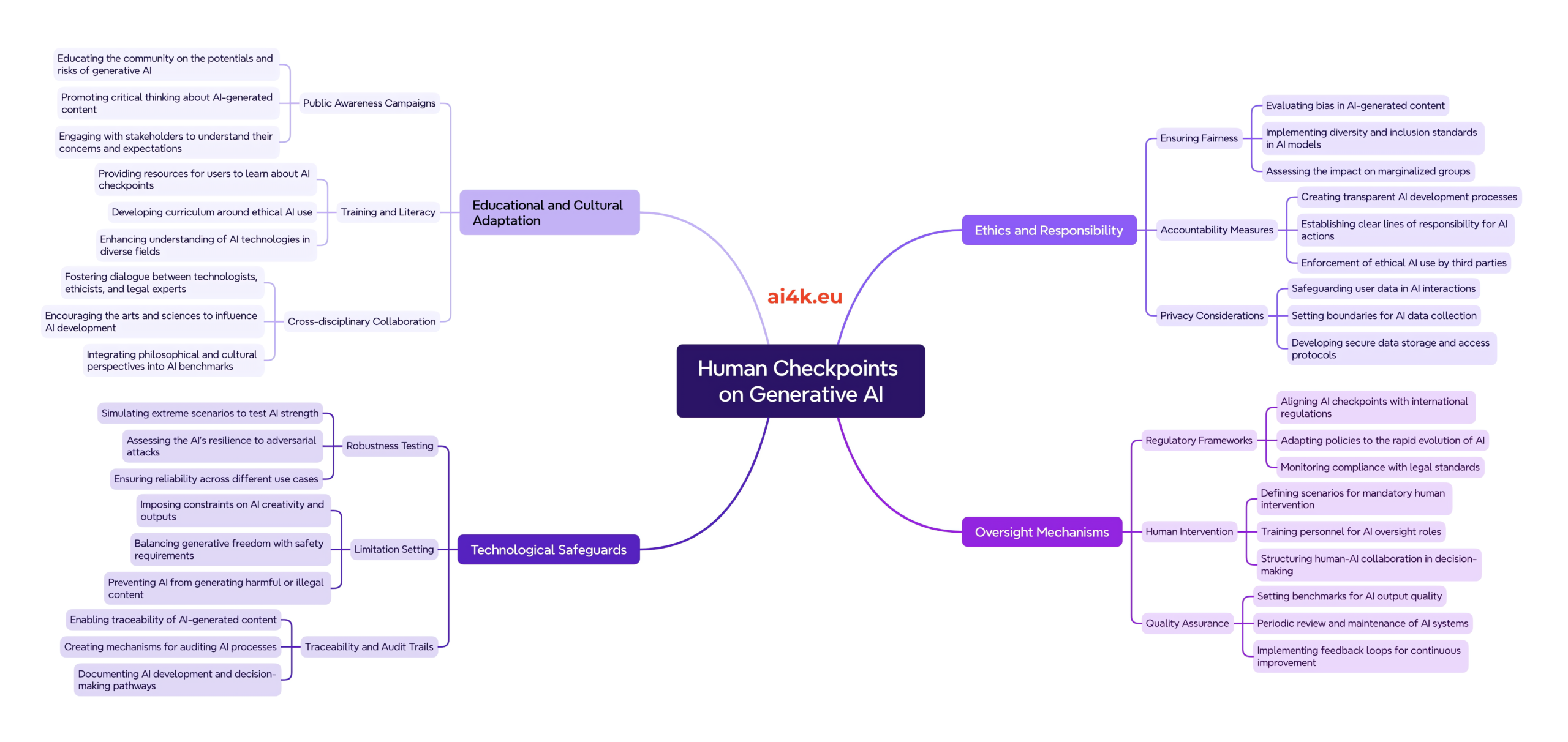
Human in the loop (HITL) refers to an approach in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning where both human intelligence and machine intelligence collaborate throughout the development and deployment process. Here are the key points:
Human in the Loop Definition
HITL involves integrating human decision-making and interaction into AI systems.
It acknowledges that certain tasks benefit from human expertise, intuition, and judgment.
Cycle of Interaction
Training
Humans curate training data, preprocess it, and guide the learning process.
Tuning
Engineers adjust model parameters, architectures, and hyperparameters based on human insights.
Testing
Human reviewers validate model performance, identify errors, and provide feedback.
Deployment
Humans monitor and maintain the system, ensuring it aligns with goals.
Use Cases
HITL is common in scenarios where:
Complex Decision-Making
AI systems lack context or domain-specific knowledge.
Ethical Considerations
Humans ensure fairness, interpretability, and compliance.
Adaptability
Systems need real-time adjustments based on changing conditions.
Examples
Content Moderation
Human reviewers verify flagged content (e.g., social media posts) alongside AI algorithms.
Autonomous Vehicles
Engineers fine-tune self-driving algorithms using human feedback.
Medical Diagnosis
Radiologists collaborate with AI tools for accurate diagnoses.
Challenges
Cost and Efficiency
Human involvement can be resource-intensive.
Bias
Humans may introduce biases during labeling or decision-making.
Balancing Automation
Striking the right balance between automation and human judgment.
AI companies are using AI
AI developers leveraging AI to formulate strategies for product promotion, devising new business models, and circumventing government regulations pose ethical and legal challenges.
While AI offers insights into consumer behavior and market trends, its use in circumventing regulations raises concerns about fairness, transparency, and legal compliance.
Businesses must prioritize ethical conduct, adhere to regulatory frameworks, and foster transparency to maintain consumer trust and uphold industry standards.
Responsible AI development ensures that innovation aligns with ethical principles and legal requirements, fostering a sustainable and trustworthy business environment.
The Real Singularity
Through cycles of iteration between AI and humans (in the loop, there at the checkpoints) to improve AI knowledge, AI will strike back with strategies to bypass regulations and continue penetrating spaces in society.
When humans can no longer rationalize what AI may be doing, when the knowledge iteration cycles have absorbed all human knowledge and exhausted human intelligence, at that precise moment the singularity will occur.
AI and the Human Intelligence
AI is surfing the Gauss curve of human intelligence, using the highest IQs in the world not only to develop the best AI tools but to participate in the iterative cycle of knowledge between AI and the human race, in other words, to outline the strategies for AI penetration into human society.
We are training the AI models to outsmart us, and that will happen according to our IQ. The smarter humans will remain coherent until their power or their ethic will define the next step.
The advance of AI is like a hurricane, it seems that it is closing the gap in systemic thinking present in humans, but what we are actually witnessing is the silence in the eye of the hurricane.
In a short time when it continues to advance, the intelligence gap will open much more, with signs that we can already see today:
We have witnessed firsthand how senior representatives of the world’s governments are embarrassed and minimized by the complexity of current AI systems.
We have also seen how the CEOs of companies like Google and Apple, who have demonstrated year after year of impeccable leadership, today appear weak and erratic in the face of relentless harassment from companies that are at the forefront of AI like OpenAI.
Those are the main signs that the fight between AI and Human Intelligence has just started.